
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Materials and Clean Energy, School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Fluid Power and Mechatronic Systems, School of Mechanical Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310030, China
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates based on chemical mechanism (CM) have received widespread attentions for the stable and repeatable signal output due to their excellent chemical stability, uniform molecular adsorption and controllable molecular orientation. However, it remains huge challenges to achieve the optimal SERS signal for diverse molecules with different band structures on the same substrate. Herein, we demonstrate a graphene oxide (GO) energy band regulation strategy through ferroelectric polarization to facilitate the charge transfer process for improving SERS activity. The Fermi level (Ef) of GO can be flexibly manipulated by adjusting the ferroelectric polarization direction or the temperature of the ferroelectric substrate. Experimentally, kelvin probe force microscopy (KPFM) is employed to quantitatively analyze the Ef of GO. Theoretically, the density functional theory calculations are also performed to verify the proposed modulation mechanism. Consequently, the SERS response of probe molecules with different band structures (R6G, CV, MB, PNTP) can be improved through polarization direction or temperature changes without the necessity to redesign the SERS substrate. This work provides a novel insight into the SERS substrate design based on CM and is expected to be applied to other two-dimensional materials.
surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) ferroelectric PMN-PT graphene oxide (GO) photo-induced charge transfer (PICT) Opto-Electronic Advances
2023, 6(11): 230094

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optics and Photonic Devices, School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
2 Institute of Data Science and Technology, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
In this paper, tin disulfide (SnS2), a two-dimensional (2D) n-type direct bandgap layered metal dichalcogenide with a gap value of 2.24 eV, was employed as a saturable absorber. Its appearance and nonlinear saturable absorption characteristics were also investigated experimentally. SnS2-PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) film was successfully prepared and employed as a mode-locker for achieving a mode-locked Er-doped fiber laser with a pulse width of 623 fs at a pulse repetition rate of 29.33 MHz. The results prove that SnS2 nanosheets will have wide potential ultrafast photonic applications due to their suitable bandgap value and excellent nonlinear saturable absorption characteristics.
Semiconductor materials Mode-locked lasers Lasers, erbium Photonics Research
2018, 6(2): 02000072
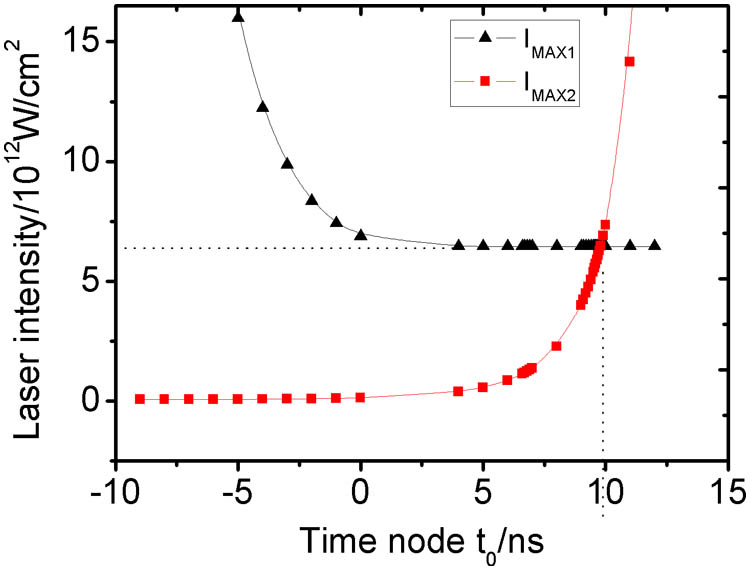
Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
The threshold of a laser-induced breakdown of air is determined experimentally and theoretically. We find that the ionization of air has two steps: the first step is a multi-photon ionization process, which provides enough “seed electrons” to initiate the next step, and the second one is predominated by cascade ionization, which continues to produce free electrons geometrically until the critical free-electron density for breakdown is reached. So a two-step model based on the Morgan ionization model is established to describe the breakdown process. It is found that the time node dividing the two steps is about 9.8 ns in atmospheric air, and the threshold derived from the two-step model proposed here is more consistent with the experimental results than traditional ionization model.
020.0020 Atomic and molecular physics 020.2070 Effects of collisions 020.4180 Multiphoton processes Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(4): 040202
1 山东师范大学物理与电子科学学院, 山东 济南 250014
2 长春理工大学理学院, 吉林 长春 130022
利用增强电荷耦合器(ICCD)光谱探测系统对飞秒激光诱导的Zn等离子体发射光谱进行时间分辨的采集和分析,研究飞秒激光等离子体光谱及其参量的时间演化特性。分析Zn等离子体的连续谱和特征谱的谱线强度随时间的演化,发现连续谱先出现且寿命只有100 ns,随后出现特征谱,对应于不同跃迁的谱强度不同。同时由谱线的展宽和强度及其跃迁能级的相关参数等得到电子密度和温度随时间的演化规律。对谱线频移进行了分析,研究发现在等离子体膨胀初期Zn原子特征谱线(ZnI) 481.0 nm的特征谱线存在较大红移,可达到0.23 nm,延时300 ns后,红移变得很小。频移随电子密度的变化近似呈线性关系。
光谱学 飞秒激光 等离子体光谱 时间演化 频移
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optics and Photonic Device, School of Physics and Electronics,Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
A molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) saturable absorber was fabricated by thermally decomposing the ammonium thiomolybdate. By using the MoS2 absorber, a compact diode-pumped passively Q-switched Tm:GdVO4 laser has been demonstrated. A stable Q-switched laser with repetition rates from 25.58 to 48.09 kHz was achieved. Maximum average output power was 100 mW with the shortest pulse duration of 0.8 μs. Maximum pulse energy is 2.08 μJ at center of 1902 nm.
Lasers Lasers Q-switched Q-switched Lasers Lasers solid-state solid-state Nonlinear optical materials Nonlinear optical materials Photonics Research
2015, 3(5): 05000256
山东师范大学物理与电子科学学院, 山东 济南 250014
利用一维辐射转移理论模型对无自蚀现象存在时Al I(394.4 nm)和Al I(396.1 nm)在不同延迟时间下的谱线进行了模拟。为使结果更为可靠,模拟过程中对模型中的参数处理方式进行了改进,最大限度地减少了独立参数的个数,在此条件下给出了能级粒子数密度随延迟时间演化的空间分布情况。通过研究该模型中粒子数空间分布半径参数对谱线线形的影响,得到了谱线自蚀深度与谱线对应上下能级粒子数密度空间分布半径比值的关系并给出了分析结果。此外还研究了频移参数对谱线线形的影响,得出了判断谱线频移的依据,并从实验上得到了验证。
光谱学 谱线模拟 一维辐射转移 频移 激光与光电子学进展
2011, 48(3): 033001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Ji'nan 250014
The vaporization threshold was measured under the irradiation of 1064-nm, 10-ns pulsed laser. Then we calculated the vaporization temperature based on the conservation law of energy and analyzed the vaporization time based on our established model. These results coincided well with the information from the micrograph of scanning electron microscope (SEM) and the spectra of the plasma. Besides, the laser ablation rate was also computed and discussed theoretically.
蒸发阈值 蒸发时间 激光烧蚀速率 140.0140 Lasers and laser optics 140.3440 Laser-induced breakdown 140.6810 Thermal effects Chinese Optics Letters
2007, 5(8): 468
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Ji'nan 250014
A Nd:YAG pulsed laser is used to ablate HgCdTe target at different ambient pressures, the emission spectrum is detected by a time- and space-resolved diagnostic technique. It is found that the characteristics of time-resolved emission spectra are influenced by the pressure of background gas. A theoretical model is developed to investigate expansion mechanism of plasma, the time evolution of the propagation distances and the velocities of plasma plume are calculated by the model at pressures of 101000, 1000, and 5 Pa, respectively. The calculated results are well consistent with the experimental data.
300.6500 Spectroscopy, time-resolved 020.3690 Line shapes and shifts 010.1320 Atmospheric transmittance 000.4430 Numerical approximation and analysis Chinese Optics Letters
2006, 4(8): 493





